Smartphones impress with the capacity numbers of their batteries. Even budget models attract attention with a 5000 mAh label on the box, and since 2024, there’s been a trend of increasing capacity to 6000 mAh. But this number is only half the truth. The reality is that your smartphone actually uses a smaller battery than stated in its specifications.
When you see a battery capacity label on your smartphone, it’s only partially true. The manufacturer isn’t lying: the battery installed in the smartphone does indeed match the stated capacity. However, the smartphone cannot use the full capacity of the battery installed in it.
Battery capacity is the amount of energy in watt-hours that the battery can provide without damaging its internal layers.
The point is that any battery is simply several layers of chemically active materials. Its electrical parameters don’t have fixed ranges. For example, it used to be considered that lithium-ion batteries should never be charged above 4.25 volts. Today, your smartphone charges its battery up to 4.4 volts.
Also, the lower discharge threshold for batteries varies. For instance, a battery can be discharged down to zero volts. But if you do this, a lithium-ion battery will swell, lose capacity, and need to be discarded. The minimum allowable voltage for a lithium-ion battery that allows it to have a long life is considered to be 2.5 volts.
Why your smartphone uses only 60% of the battery’s capacity
The standard operating range for a lithium-ion battery is considered to be from 2.5 to 4.25 volts. For the past few years, the standard has been 2.5-4.4 volts.
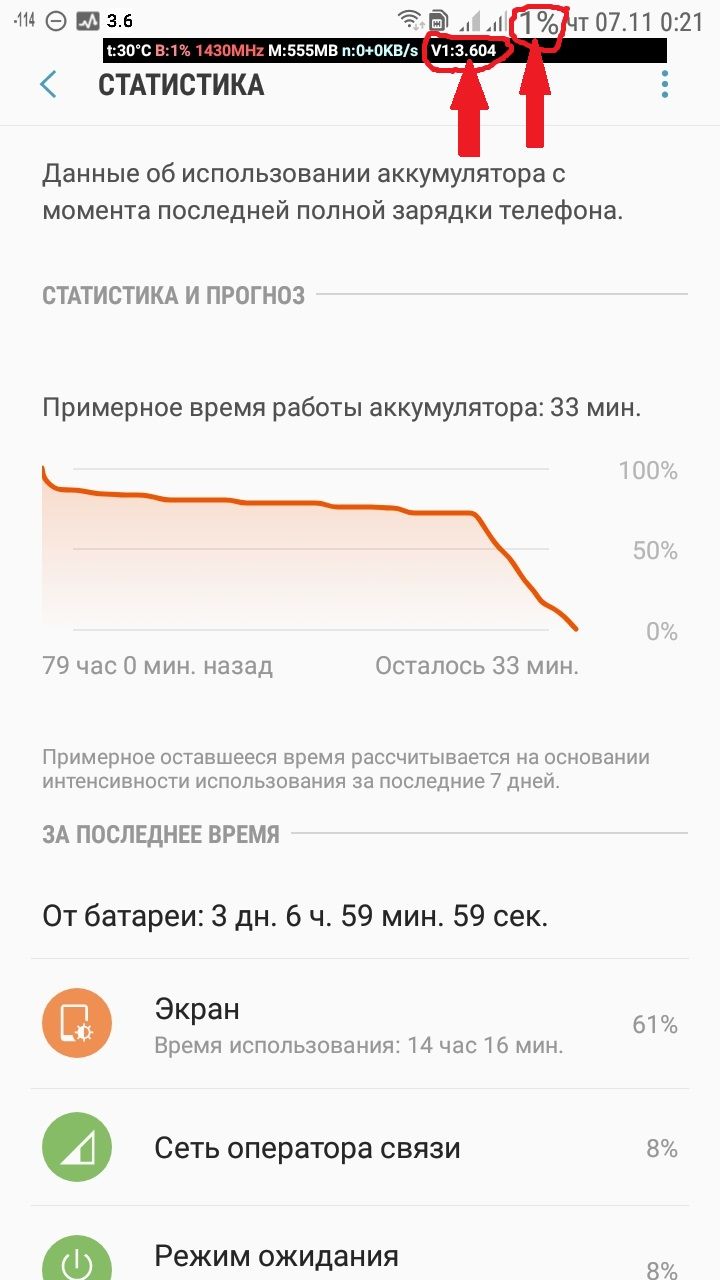
However, your smartphone shows 0% charge and turns off when the lithium-ion battery’s voltage reaches 3.6 volts.
This means that the operating range of your smartphone battery is not 2.5-4.4 volts but 3.6-4.4 volts. This range provides approximately 60% of the stated capacity.
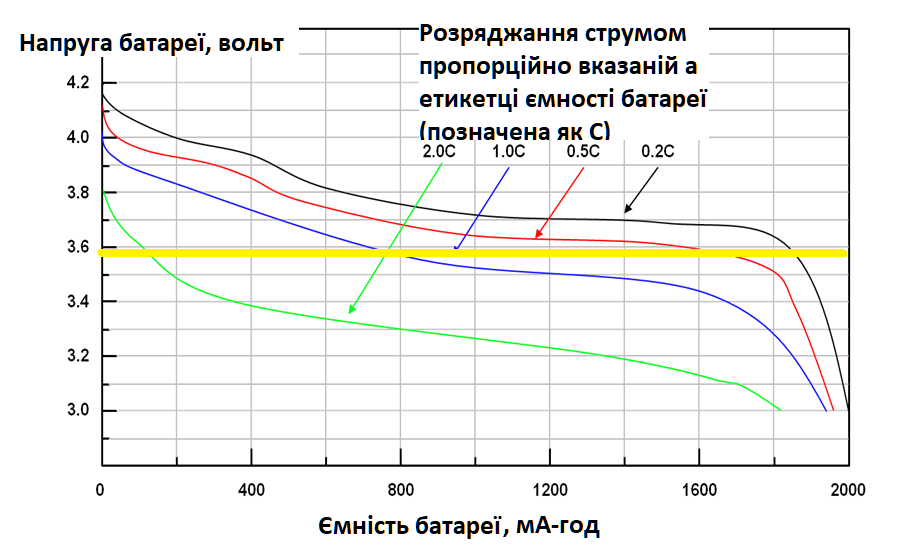
Look at the chart below. It shows several colored curves, each indicating battery capacity depending on the current used to discharge it. For example, when you scroll through social media feeds with the screen at minimum brightness, the battery discharges with a current of 0.2C or 0.5C. During gaming, the battery discharges at 1C or 2C. In any case, your smartphone can only use the battery capacity above the yellow line. The capacity below the yellow line cannot be used by your smartphone.
For instance, if your smartphone has a 10,000 mAh battery, it will show a full discharge and turn off after using only 5,600 mAh. This is the capacity provided by a 10,000 mAh battery before reaching 3.6 volts.
The remaining 3,400 mAh is available if the battery is discharged from 3.6 volts down to 2.5 volts. But smartphones don’t do this and shut down at 3.6 volts.
If your smartphone battery has a capacity of 5,000 mAh, it actually uses 3,400 mAh. The rest of the capacity is not accessible to your smartphone.
You can easily verify that your smartphone shuts down when the battery voltage drops to 3.6 volts by using the BatteryVoltage app.
Not only smartphones use only a portion of the battery capacity
The 3.6-volt minimum voltage level applies not only to smartphones. This appears to be a standard in electronics. Laptops and tablets, for example, also turn off when the battery discharges to only 3.6 volts.
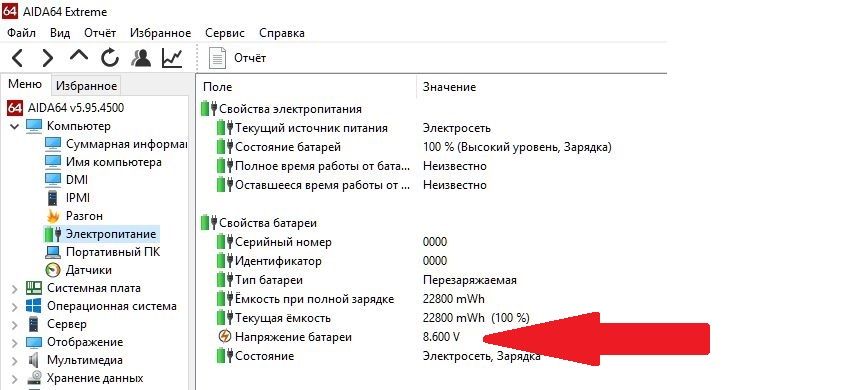
You can verify that your laptop shuts down when the battery voltage reaches 3.6 volts in its cells using the AIDA64 application, which can show the battery voltage.
In laptops, the battery contains 2, 3, or sometimes 4 cells connected in series. A laptop with 2 cells will turn off at a battery voltage of 7.2 volts, a laptop with three cells will turn off at 10.8 volts, and a laptop with four cells will turn off at 14.4 volts.
These figures also apply to tablets, which can have a battery of one, two, or three cells.
Which gadgets fully discharge the battery?
Experiments show that of consumer electronics, only power banks use the full capacity of their battery. Power banks with lithium-ion batteries charge the battery up to a maximum of 4.25 (sometimes 4.4) volts and turn off when the battery discharges to 3.0 (sometimes 2.7) volts.
The 3.0-2.5 volt range provides very little capacity, so it is often ignored. Discharging the battery only to 3.0 volts instead of 2.5 volts can slightly extend the charging cycles of the battery.
Power banks have to discharge lithium-ion batteries below 3.6 volts to compensate for voltage conversion losses and increase it to the level required by USB. These losses usually account for about 30%. That’s why a power bank with a capacity of 10,000 mAh will actually provide about 6,000 mAh.